What is Data Engineering??
Data Engineering is the practice of designing and building systems for the aggregation, storage, and processing of large volumes of data to make it available for downstream users.
Key elements of data engineering
-
Data Extraction/collection: Process of collecting raw data from various sources. This includes everything from structured data[in tabular format] to un-structured data[text, images, etc.].
-
Data Ingestion: The process of transferring and loading data into a target system in a reliable and repeated way.
-
Data Storage: Data Engineers design the necessary storage solutions to Store the Ingested data.
-
Data Transformation: To make the data useful for data scientists, enabling them to perform their analysis.
- ETL vs ELT:
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Transformation happens before loading into storage systems.
- ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): Transformation happens after loading into the storage systems.
- ETL vs ELT:
-
Data Quality & Validation:
- Data Quality: refers to the level of accuracy, consistency, completeness, and relevance of the data collected, stored, and used in an organisation. Maintaining high data quality is crucial for effective decision making. This is where Data Validation comes into play.
- Data Validation: Data validation is the process of verifying the collected data is accurate, complete, consistent, and relevant before it’s been stored and used further.
-
Data Serving: Once the data has been collected and processed, it’s delivered to the end user.
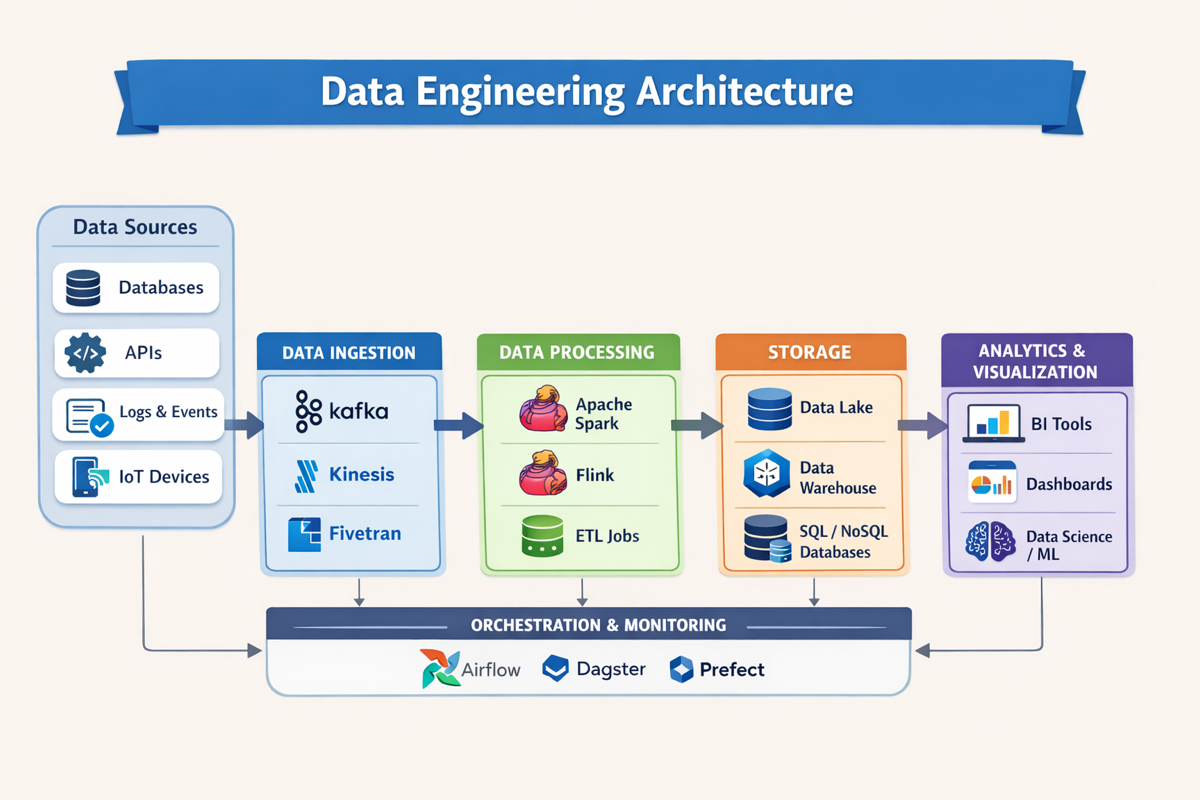
Data Engineering Architecture
-
Data sources: Data can be collected or generated through various sources. These sources may vary in structure, velocity and volume. Some of the most common data sources are as follows:
- Relational Databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.
- APIs
- XML, JSON, CSV files
- Mobile apps
- Surveys and Interviews.
- Smart Sensors
-
Ingestion layer: Refers to the process of collecting raw, unstructured data from various sources and transferring it into a target storage system for processing and analysing.
It is the first step in any data pipeline. -
Processing layer: This layer consists of tools and technologies that processes the ingested raw data into usable or structured form, enabling it to be futher used for analytics, and decision making.
-
Storage layer: This layer is responsible for continuously storing and managing data. In modern data architectures, it often uses distributed file systems for handling large volumes of data.
-
Serving layer: Serving layer (also known as Data Serving) is the process of making the processed data available for end users and applications.
What do data engineers do?
Data Engineering involves many tasks, such as:
- Collecting data from various sources (apps, websites, etc.)
- Moving data to target destination.
- Storing unorganised raw data in a structured and organised manner.
- Validating and processing Big Data.
- Build data pipelines.
- Design Data storage systems.
Data Engineering vs Data Science vs Data Analysis
Data Engineers: Data Engineers build and maintain data infrastructures to automate data ingestion, creation, storage and processing.
Data Scientists: Data Scientists build and use machine learning models, data exploration and other technologies to predict future outcomes.
Data Analysts: Data Analysts examine large datasets to identify trends and extract insights to help organisation make data-driven decisions. They work with predefined datasets.
Data Pipelines
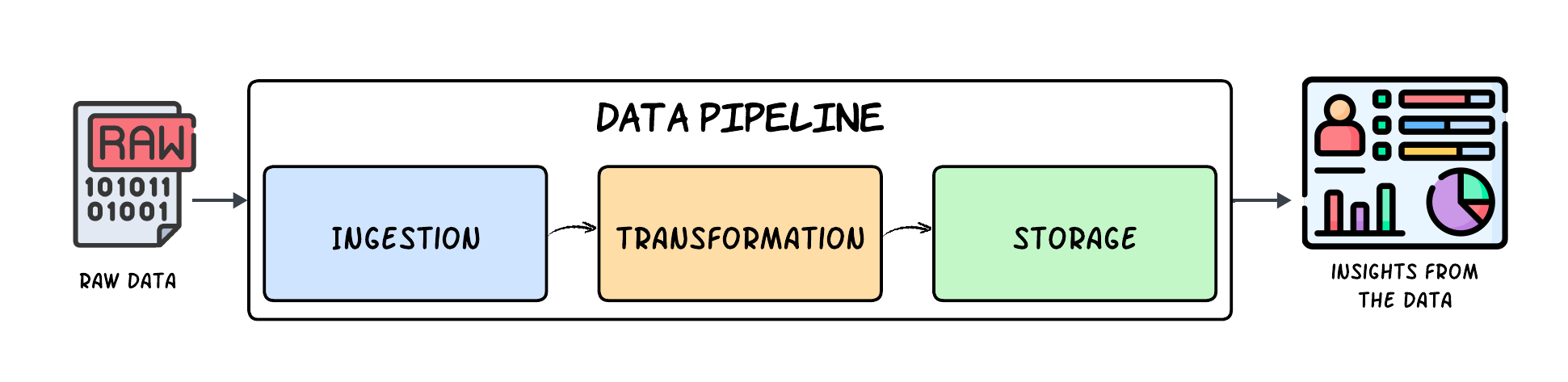
What is a Data Pipeline
Data pipeline is a method in which raw data from various sources is ingested, transformed and then moved to a target destination, such as data lake or data warehouse, for analysis.
Types of Data Pipelines
There are mainly two types of data pipelines:
- Batch data pipeline: In Batch processing data pipeline, data is processed in large volumes or batches. It’s often cost-efficient and mostly used for very large amount of data.
It performs a series of commands on every batch of data in sequence and gives output. after all the data processing is complete, it loads the entire batch into a cloud storage.
- Streaming data pipeline: Streaming data pipelines processes raw data almost instantly. It processes the data in real time as it is generated. It processes data even if some data packets are lost or delayed.
Streaming pipelines process a series of events for real-time analysis.
Batch vs Streaming data pipelines
| Feature | Batch Pipeline | Streaming Pipeline |
|---|---|---|
| Data arrival | Data is collected first, then processed | Data is processed the moment it arrives |
| Processing time | Runs after fixed time intervals | Runs continuously |
| Latency | High (minutes to hours) | Low (milliseconds to seconds) |
| Use cases | Reports, backups, billing | Live dashboards, alerts, monitoring |
| Complexity | Simpler to build and maintain | More complex |
| Cost | Cheaper | Expensive |
| Data volume | Large historical datasets | Continuous data flow |
| Examples | Daily sales report | Online games |
Big Data Storage Systems
After data is processed, it must be stored in durable, secure, and scalable storage systems for future analysis and use.
Two commonly used big data storage systems are data lakes and data warehouses.
Data Warehouses
A data warehouse is an enterprise data platform, also called Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW). It is used to aggregate data from various sources into a central database optimised for querying and analysis of the data.
A data warehouse can store both current and historical data in one place and is built to give a long-term insight over time.
Data Marts
A data mart is a subset of a data warehouse that contains data needed by a specific business function, department, or selected group of users within an organisation.
Data marts are used to analyse department-specific information more efficiently
Data Lakes
Data lake is a storage repository which is designed to store a large amount of raw data that can be structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. Once the data reaches the data lake, it can be used for machine learning or training AI models.
Data Lakehouse
A Data lakehouse is a data architecture that combines the flexible storage of data lakes with the analytical performance of data warehouses.
Data Modeling
Data modeling is the process of creating a visual representation or a blueprint of data and its relationships. It shows how data is structured, stored, and accessed
so it can be understood, stored efficiently, and utilised correctly by applications and analytics.
Importance of Data Modeling?
Modern organizations generate large amounts of raw data. Before this data can be analyzed and turned into insights, it needs to be properly structured. Data modeling helps by visually defining how data is organized and related, making it easier to store, manage, and use for decision-making.
Common Tools Used in Data Engineering
- Ingestion
- AWS Kinesis
- Apache Kafka
- Processing
- Hadoop
- Apache Spark
- Storage
- PostgreSQL
- Amazon S3
- BigQuery
- Orchestration
- Apache Airflow